
"I have used a wide variety of secondaries and Jackson ImmunoResearch has consistently been the best. The fluorophores are bright and stable and their selective (x reactivity removed) secondaries have always shown species specificity in multiple labeling."
Janet Duerr, Ohio UniversityRating: 5.0
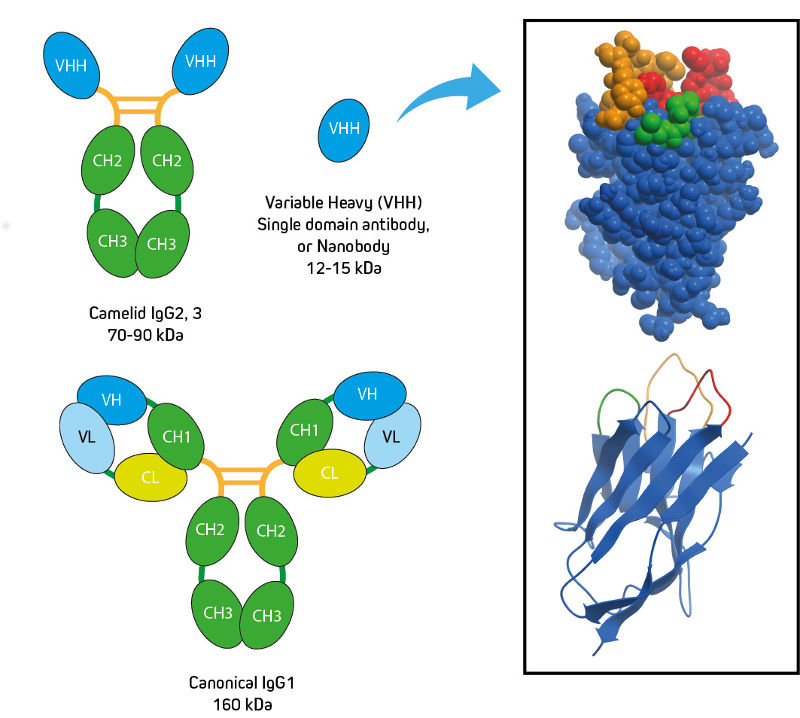
Camelids (alpaca, llama, camel, vicuna and guanaco) produce two non-canonical immunoglobulins alongside the conventional IgG1. IgG2 and IgG3 are known as heavy chain only (or heavy chain) antibodies. They have single domain binding sites (VHH), and do not contain CH1 domains or light chains (Figure 1).
Jackson ImmunoResearch offers a range of secondary antibodies utilizing the properties of camelid immunoglobulins, for detection in assays and to expedite NANOBODY® development. We also provide camelid-derived secondaries, including AffiniPure-VHH® Secondary Antibodies.

VHH antibodies (NANOBODIES®) are rapidly being adopted in a variety of fields. Uses for these novel antibodies include various applications such as medical diagnostics, therapeutics, biosensors, crystallization partners, and detection of small molecules.
VHH antibodies are derived from the VHH domain of heavy chain-only immunoglobulins (IgG subclasses 2 and 3) from camelid species. VHH libraries derived from a camelid host animal (typically alpaca or llama) are screened for target specificity, and the desired VHH sequences are obtained. Recombinant VHH (rVHH) can then be produced in an expression system of choice. The long CDRs shown in the ribbon diagram (Figure 1) are characteristic of the VHH domain, and provide the antibody access to recessed antigenic sites not available to canonical antibodies.
The 12-15 kDa antigen-binding VHH domain acts as a framework for recombinant antibody production. VHH antibodies can be designed in a variety of structural formats.
The small size and long CDR3 loop of the VHH antibodies allows better access to cryptic epitopes compared to conventional antibodies.
VHH antibodies have good solubility and are stable to heat, proteases and pH extremes.
VHH antibodies can cross the bloodbrain barrier and access other remote locations, making them useful for drug delivery. They also clear quickly from circulation and are relatively non-immunogenic to humans (Bannas et al, 2017). Good stability allows delivery via a variety of routes, including intravenous and subcutaneous injection, nasal inhalation and oral ingestion.
VHH antibodies are easy to clone and modify. They can be produced recombinantly at high levels in bacterial, yeast, and mammalian expression systems. Their design can include tags for purification, or functional groups to enable the addition of drugs or fluorescent probes.