Immuno Techniques
Secondary antibodies are widely used in a wide range of research applications. In these articles we describe both conventional and innovative techniques, and how secondary antibodies can be used to get more from your assays.
Posts

Autofluorescence
Autofluorescence can present challenges for techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and flow cytometry, …Read More »
Fluorogenic DNA-PAINT: Modifying DNA-PAINT For Faster Super-Resolution Imaging
DNA-based Point Accumulation for Imaging in Nanoscale Topography (DNA-PAINT) is an increasingly popular super-resolution microscopy …Read More »
The Evolution of DNA-PAINT
First reported in 2010, DNA points accumulation for imaging in nanoscale topography (DNA-PAINT) is a …Read More »
Why use a particular Antibody format?
Here, we discuss the differences between the different antibody formats available, including H+L, F(ab′)2, Fab, …Read More »
Imaging with Jackson ImmunoResearch Secondary Antibodies
Imaging using immunostaining is a commonly used technique that can elucidate many details about how …Read More »
Selecting a Secondary Antibody for Bead-Based Applications
Many different bead-based applications have been developed for detecting and purifying biomolecules. Secondary antibodies have …Read More »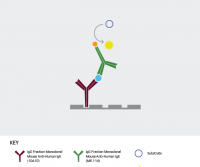
Tips for Selecting the Right Secondary Antibody
Secondary antibodies offer many advantages for scientific research. These include increased assay sensitivity, owing to …Read More »
Far-Red and Near Infrared Dyes
Antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes are essential tools for a broad range of research techniques, …Read More »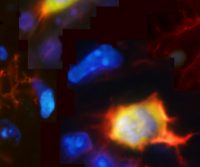
An Introduction to Spatial Biology
Spatial biology is a rapidly evolving field of research that puts cellular information into its …Read More »
Selecting the Right Fluorescently-Labeled Secondary Antibody for Spatial Proteomics
Conventional IHC, CycIF, and t-CyCIF can all be performed using fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies, provided …Read More »
abberior Flux dyes and JIR AffiniPure-VHH™ antibodies
Indirect immunofluorescence staining is a pivotal method for biomolecule labeling, yet its efficacy for super …Read More »
What is an Antibody?
Antibodies are complex proteins produced by mammalian B cells during the adaptive immune response. Their …Read More »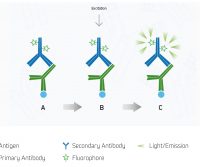
Secondary detection: Indirect detection set-up
Secondary detection, also known as indirect detection, has two important advantages over direct detection. These …Read More »
Top 10 Tips for ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) remains one of the most popular immunoassay techniques due to its …Read More »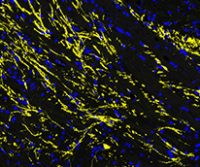
Considerations for Multiplex Immunofluorescence
A major advantage of fluorescent detection is that it allows for multiplexing. Depending on the …Read More »
Bead-based multiplexing assays: Luminex® xMAP® Technology
According to Luminex® (a DiaSorin company), xMAP® is the world′s most used multiplexing technology, a …Read More »
Tissue Clearing Techniques
The term ‘tissue clearing’ describes a collection of techniques used for making large, fixed biological …Read More »
Assay Setup: Sandwich ELISA for Allergy
ELISA is a widely used technique for detecting and quantifying one or more specific proteins …Read More »
Super-Resolution Microscopy: Principles, Technologies, and Considerations for Reagent Selection
While conventional microscopy techniques are still widely used for scientific research, super-resolution microscopy (SRM) is …Read More »
ELISA Guide; Part 4: Troubleshooting
Overview No Signal or Weak Signal High Background Poor Reproducibility Between Plates Poor Reproducibility Between …Read More »
AffiniPure-VHH® secondary antibodies for flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique used to analyze individual cells in suspension. It uses a …Read More »
ELISA Guide; Part 3: ELISA Optimization
Overview Optimization Controls and Standards Validation Spike and Recovery Dilutional Linearity Parallelism Data Analysis Optimization …Read More »
NEW: 4 part ELISA Guide

An Introduction to Surface Plasmon Resonance
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is a label-free optical biosensing technique that allows researchers to measure …Read More »
ELISA Guide; Part 2: The ELISA Protocol
Overview Key Stages in the ELISA Protocol Capture Sample Preparation Analyte-Specific Antibody Considerations Secondary Antibody …Read More »
Western Blotting Guide

ELISA Guide; Part 1: Introduction to ELISA, Formats and Signal Amplification
Introduction to ELISA Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was first described in 1971 when it was …Read More »
The Rise of Antibody Therapeutics
In June 1986, muromonab-CD3 became the first monoclonal antibody approved by the U.S. Food and …Read More »
CAR T-Cell Therapy: Features, Benefits, and Applications
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is fast becoming established as the fifth pillar of …Read More »
Detecting ScFVs – Considerations for optimal detection
Single chain variable fragments (scFvs) are commonly used in CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell) cell …Read More »
Western blotting guide: Part 8, Visualization
Visualization of the target proteins is the object of a western blot. There are a …Read More »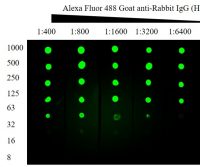
Dot Blot: A Quick and Easy Method for Separation-Free Protein Detection
Dot blot is one of the easiest ways to determine whether a protein of interest …Read More »
Vial fill size, protein concentration, and reconstitution volumes
We are sometimes asked about the discrepancy between the protein concentration recorded, the recommended volume …Read More »
Troubleshooting: Using Anti-Light Chain Antibodies after Immunoprecipitation
Anti-light chain antibodies are commonly used for Western blotting (WB) after Immunoprecipitation (IP) when detecting …Read More »
Western blotting guide: Part 7, Membrane Washing
Washing removes unbound or aggregated proteins present on the blot as well as unbound reagents …Read More »
Lateral Flow Immunoassay: Methodology, Applications, and Considerations for Use
Lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) is a membrane-based technique for detecting specific analytes in complex samples. …Read More »
Western blotting guide: Part 6, Secondary Antibodies
The secondary antibody detects the primary antibody, typically conjugated to a reporter molecule it enables …Read More »
Western blotting guide: Part 5, Primary Antibodies
Primary antibodies are used to detect the protein of interest. Part 5 of the Western …Read More »
Western blotting guide: Part 4, Membrane blocking
Blocking is essential to prevent non-specific interactions between the transferred proteins, the membrane and the …Read More »
Benefits of Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Point-Of-Care Testing
Lateral flow immunoassays (LFIA) are widely used for rapid detection of specific analytes in a …Read More »
Selecting Fluorophores for Antibody-based Research
Fluorophores are essential tools for scientific research. They are widely used for immunoassay techniques such …Read More »
Lateral flow tests for diagnostics
Lateral flow assays are one of the many types of immunoassays available for health monitoring. …Read More »
Serological testing for diagnostics and disease surveillance
Serological tests enable disease surveillance from initial infection through to the development of immunity against …Read More »
Chromogenic Detection for Western Blot, IHC, and ELISA
Chromogenic substrates are used in colorimetric detection. They are simple and easy to use. Suitable …Read More »
Colorimetric Western blotting
Colorimetric detection is an economical and simple method for the detection of analyte when Western …Read More »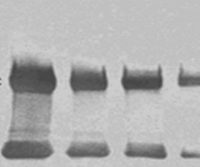
Chemiluminescent Western blotting
Chemiluminescent Western blotting is a highly sensitive protein detection method. The broad dynamic range allows …Read More »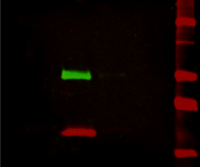
Fluorescent Western blotting
Fluorescent Western blotting can offer many advantages to an already robust protein detection technique. Secondary …Read More »
Conjugates for Western blotting
3 methods of detection are available for Western blotting: colorimetric, chemiluminescent and fluorescent. Each detection …Read More »
Direct and Indirect Western blotting
Western blotting is a robust technique employing antibodies to detect proteins immobilized on a blotting …Read More »


